| [1] Angulo P.GI epidemiology: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.2007;25(8):883-889.
[2] Williams R.Global challenges in liver disease.Hepatology. 2006; 44(3):521-526.
[3] Fan JG,Zhu J,Li XJ,et al.Prevalence of and risk factors for fatty liver in a general population of Shanghai,China.J Hepatol. 2005;43(3):508-514.
[4] Fan JG,Farrell GC.Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China. J Hepatol.2009;50(1):204-210.
[5] 中华医学会肝病学分会脂肪肝和酒精性肝病学组.非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊疗指南[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2010,18(3):163-166.
[6] Rabe K,Lehrke M,Parhofer KG,et al.Adipokines and insulin resistance.Mol Med. 2008;14(11-12):741-751.
[7] Yang Q,Graham TE,Mody N,et al.Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes.Nature.2005;436(7049): 356-362.
[8] Stefan N,Hennige AM,Staiger H,et al.High circulating retinol binding protein 4 is associated with elevated liver fat but not with total, subcutaneous,visceral, or intramyocellular fat in humans.Diabetes Care.2007;30:1173-1178.
[9] Terra X,Auguet T,Broch M,et al.Retinol Binding Protein-4 Circulating Levels Were Higher in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Vs.Histologically Normal Liver From Morbidly Obese Women.Obesity,2012.
[10] Tan Y,Sun LQ,Kamal MA,et al.Suppression of retinol-binding protein 4 with RNA oligonucleotide prevents high-fat diet- induced metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta.2011; 1811(12): 1045-1053.
[11] Cengiz C,Ardicoglu Y,Bulut S,et al.Serum retinol-binding protein 4 in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: does it have a significant impact on pathogenesis? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.2010;22(7):813-819.
[12] Schina M,Koskinas J,Tiniakos D,et al.Circulating and liver tissue levels of retinol-binding protein-4 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatol Res.2009;39(10):972-978.
[13] ]Nobili V,Alkhouri N,Alisi A,et al.Retinol-binding protein 4: a promising circulating marker of liver damage in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7(5):575-579.
[14] Alkhouri N,Lopez R,Berk M,et al.Serum retinol-binding protein 4 levels in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.J Clin Gastroenterol.2009;43(10): 985-989.
[15] Schattenberg JM,Schuppan D.Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: the therapeutic challenge of a global epidemic.Curr Opin Lipidol.2011;22(6):479-488.
[16] Mazza A,Fruci B,Garinis GA,et al.The role of metformin in the management of NAFLD. Exp Diabetes Res.2012;2012: 716404.
[17] Sofer E,Boaz M,Matas Z,et al.Treatment with insulin sensitizer metformin improves arterial properties, metabolic parameters, and liver function in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Metabolism.2011;60(9):1278-1284.
[18] Anstee QM,Goldin RD.Mouse models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis research.Int J Exp Path. 2006;87:1-16.
[19] Kajikawa S,Harada T,Kawashima A,et al.Suppression of hepatic fat accumulation by highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid prevents the progression of d-galactosamine-induced hepatitis in mice fed with a high-fat/high-sucrose diet. Biochim Biophys Acta.2009;1791(4):281-288.
[20] Safwat GM,Pisanò S,D'amore E,et al.Induction of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance by feeding a high-fat diet in rats: does coenzyme Q monomethyl ether have a modulatory effect? Nutrition.2009;25(11-12): 1157-1168.
[21] Ratziu V,Poynard T.Assessing the outcome of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? It's time to get serious.Hepatology.2006; 44(4):802-805.
[22] Kleiner DE,Brunt EM,Van Natta M,et al.Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatology.2005;41(6): 1313-1321.
[23] Blomhoff R,Blomhoff HK.Overview of retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol, 2006;66(7):606-630.
[24] Hanley AJ,Williams K,Festa A,et al.Liver markers and development of the metabolic syndrome. DIabetes. 2005; 54: 3140-3147.
[25] Tonjes A,Bluher M,Stumvoll M.Retinol-binding protein 4 and new adipocytokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Current Pharmaccutical Design.2010;16:1921-1928.
[26] Quadro L,Hamberger L,Colantuoni V,et al.Understanding the physiological role of retinol-binding protein in vitamin A metabolism using transgenic and knockout mouse models. Mol Aspects Med.2003;24(6):421-430.
[27] Smeland S,Bjerknes T,Malaba L,et al.Tissue distribution of the receptor for plasma retinol -binding protein. Biochem J.1995;305:419-424.
[28] Romanowska A,Lebensztejn DM,Skiba E,et al.Retinol binding protein-4 as a serum biomarker of intrahepatic lipid content in obese children--preliminary report.Acta Biochim Pol. 2011; 58(1):35-38.
[29] Milner KL,Van Der Poorten D,Xu A,et al.Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein levels relate to inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.2009; 49(6): 1926-1934.
[30] Brandauer J,Landers-Ramos RQ,Jenkins NT,et al.Effects of prior acute exercise on circulating cytokine concentration responses to a high-fat meal.Physiological Reports.2013; 1(3):e00040.
[31] Lewis JG,Shand BI,Elder PA,et al.Plasma retinol-binding protein is unlikely to be a useful marker of insulin resistance. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.2008;80(1): e13-15.
[32] He L,Sabet A,Djedjos S,et al.Metformin and insulin suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis through phosphorylation of CREB binding protein.Cell.2009;137(4): 635-646.
[33] Musso G,Cassader M,Rosina F,et al.Impact of current treatments on liver disease, glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials.Diabetologia. 2012;55(4):885-904.
[34] Loomba R,Lutchman G,Kleiner DE,et al.Clinical trial: pilot study of metformin for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.2009;29(2):172-182.
[35] Francque SM,Verrijken A,Mertens I,et al.Noninvasive assessment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese or overweight patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.2012; 10(10):1162-1168.
[36] Garinis GA,Fruci B,Mazza A,et al.Metformin versus dietary treatment in nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis: a randomized study.Int J Obes (Lond).2010;34(8):1255-1264.
[37] Nar A,Gedik O.The effect of metformin on leptin in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Acta Diabetol.2009;46(2):113-118.
[38] Abenavoli L.Metformin: a therapeutic option for treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Dig Dis Sci.2010;55(7):2121.
[39] Raso GM,Esposito E,Iacono A,et al.Comparative therapeutic effects of metformin and vitamin E in a model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the young rat.Eur J Pharmacol.2009; 604 (1-3):125-131.
[40] Avramoglu RK,Basciano H,Adeli K.Lipid and lipoprotein dysregulation in insulin resistant states. Clin Chim Acta.2006; 368(1-2):1-19. |
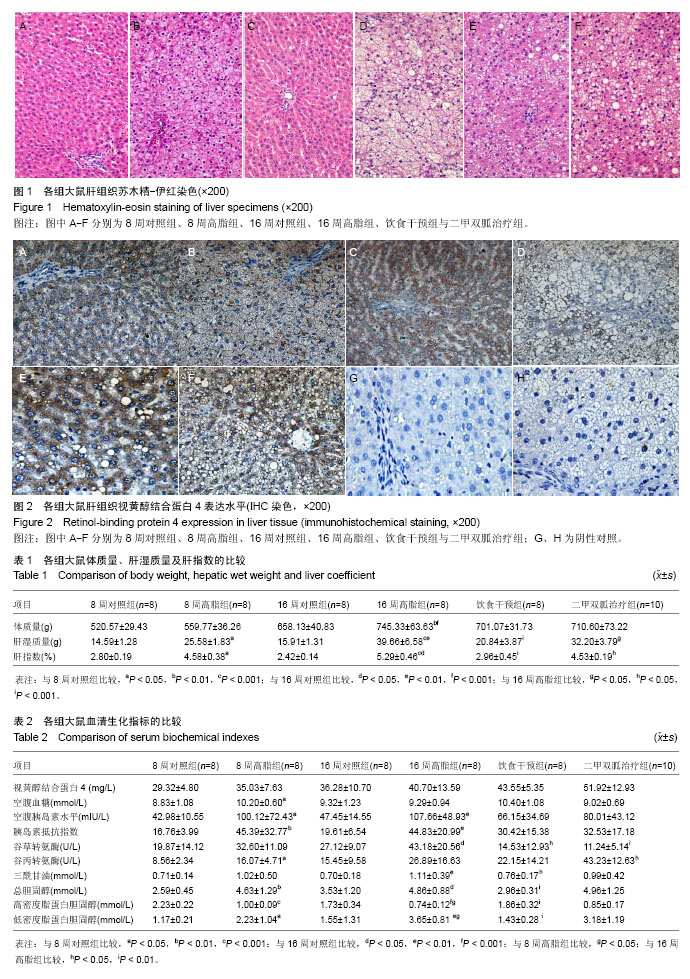
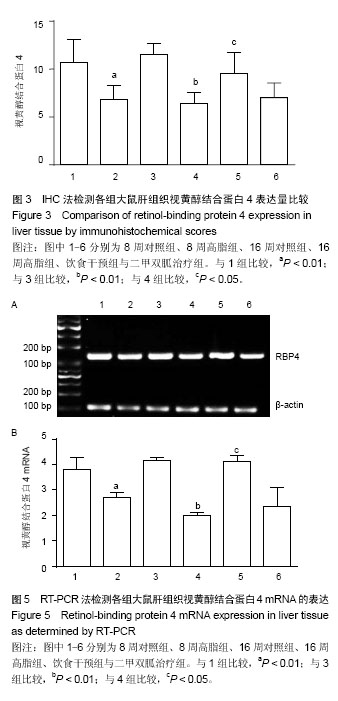
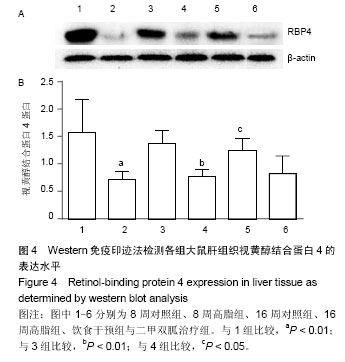
.jpg)
.jpg)